Reading-Notes-for-Advanced-Software-Development-in-Python-Course
Python Scope
Not all variables can be accessed from anywhere in a program. The part of a program where a variable is accessible is called its scope. There are four major types of variable scope and is the basis for the LEGB rule. LEGB stands for Local -> Enclosing -> Global -> Built-in.
Namespaces : A namespace is a container where names are mapped to objects, they are used to avoid confusions in cases where same names exist in different namespaces. They are created by modules, functions, classes etc.
Scope : A scope defines the hierarchical order in which the namespaces have to be searched in order to obtain the mappings of name-to-object(variables). It is a context in which variables exist and from which they are referenced. It defines the accessibility and the lifetime of a variable.
LEGB Rule

In Python, the LEGB rule is used to decide the order in which the namespaces are to be searched for scope resolution.
The scopes are listed below in terms of hierarchy(highest to lowest/narrowest to broadest):
- Local(L): Defined inside function/class
- Enclosed(E): Defined inside enclosing functions(Nested function concept)
- Global(G): Defined at the uppermost level
- Built-in(B): Reserved names in Python builtin modules
Local Scope
Whenever you define a variable within a function, its scope lies only within the function. It is accessible from the point at which it is defined until the end of the function and exists for as long as the function is executing (Source). Which means its value cannot be changed or even accessed from outside the function.
The Global Scope
Whenever a variable is defined outside any function, it becomes a global variable, and its scope is anywhere within the program. Which means it can be used by any function.
There’s only one global Python scope per program execution. This scope remains in existence until the program terminates and all its names are forgotten.
To inspect the names within your main global scope, you can use dir(). If you call dir() without arguments, then you’ll get the list of names that live in your current global scope.
Built-in Scope
This is the widest scope that exists! All the special reserved keywords fall under this scope. We can call the keywords anywhere within our program without having to define them before use.
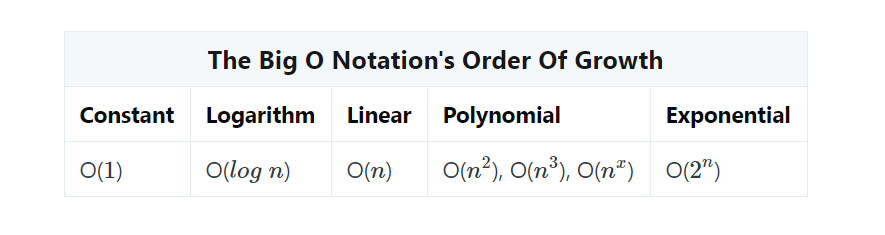
Big O Notation
In computer science, time complexity is the computational complexity that describes the amount of time it takes to run an algorithm.
Big O notation is a method for determining how fast an algorithm is. Using Big O notation, we can learn whether our algorithm is fast or slow. This knowledge lets us design better algorithms.
Big O takes the upper bound. The worst-case results in the worst execution of the algorithm.
Where the further right they are, the longer it takes. n is the size of the input. Big O notation uses these functions to describe algorithm efficiency.