Reading-Notes-for-Advanced-Software-Development-in-Python-Course
Random Module
The Python standard library provides a module called random that offers a suite of functions for generating random numbers.
Random functions
The Random module contains some very useful functions listed bellow.
Randint
Usage: Generates random integer values. This function takes two arguments: the start and the end of the range for the generated integer values. Random integers are generated within and including the start and end of range values, specifically in the interval [start, end]. Random values are drawn from a uniform distribution.
Syntax:
import random
print random.randint(0, 5)
Choice
Usage: Random numbers can be used to randomly choose an item from a list.
Syntax:
import random
myList = [2, 109, False, 10, "Lorem", 482, "Ipsum"]
random.choice(myList)
Shuffle
Usage: Randomness can be used to shuffle a list of items, like shuffling a deck of cards. The shuffle() function can be used to shuffle a list. The shuffle is performed in place, meaning that the list provided as an argument to the shuffle() function is shuffled rather than a shuffled copy of the list being made and returned.
Syntax:
from random import shuffle
x = [[i] for i in range(10)]
shuffle(x)
Randrange
Usage: Generate a randomly selected element from range(start, stop, step)
random.randrange(start, stop[, step])
Syntax:
import random
for i in range(3):
print random.randrange(0, 101, 5)
Risk Analysis in Software Testing

Risk Analysis is very essential for software testing. In software testing, risk analysis is the process of identifying risks in applications and prioritizing them to test.
Risk analysis is the process of identifying the risks inapplications or software that you built and prioritizingthem to test.
Why Perform Risk Analysis in Software Testing?
Because finding defects in production is expensive! The key reason why people perform risk analysis during software testing is to better understand what can really go wrong with an application before it goes into production. A risk analysis performed during software testing helps to identify areas where software flaws could result in serious issues in production. By identifying areas of concern early, developers are able to proactively remediate and reduce the overall risk of a production defect.
Risk management includes the following tasks:
- Identify risks and their triggers
- Classify and prioritize all risks
- Craft a plan that links each risk to a mitigation
- Monitor for risk triggers during the project
- Implement the mitigating action if any risk materializes
- Communicate risk status throughout project
Risk Identification
There can be different type of risks include as follows:
-
Software Risks: Knowledge of the most common risks associated with Software development, and the platform you are working on.
-
Business Risks: Most common risks associated with the business using the Software.
-
Testing Risks: Knowledge of the most common risks associated with Software Testing for the platform you are working on, tools being used, and test methods being applied.
-
Premature Release Risk: Ability to determine the risk associated with releasing unsatisfactory or untested Software Products.
-
Risk Methods: Strategies and approaches for identifying risks or problems associated with implementing and operating information technology, products and process; assessing their likelihood, and initiating strategies to test those risks.
After identifying the risks associated with your software, the next step is to assess the risks; i.e, Risk Assessment.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment may be the most important step in the risk management process, and may also be the most difficult and prone to error. Once risks have been identified and assessed, the steps to properly deal with them are much more programmatically.
How to perform Risk Analysis?
There are three steps:
-
Searching the risk
-
Analyzing the impact of each individual risk
-
Measures for the risk identified
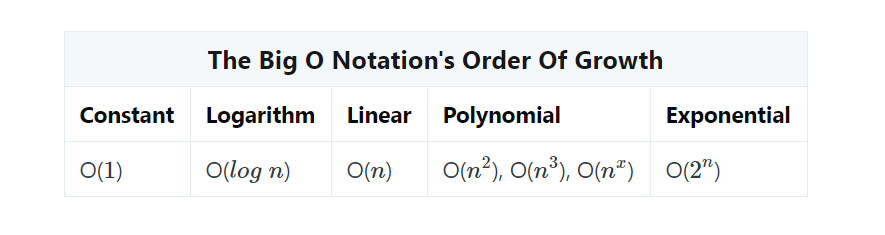
Big O Notation
In computer science, time complexity is the computational complexity that describes the amount of time it takes to run an algorithm.
Big O notation is a method for determining how fast an algorithm is. Using Big O notation, we can learn whether our algorithm is fast or slow. This knowledge lets us design better algorithms.
Big O takes the upper bound. The worst-case results in the worst execution of the algorithm.
Where the further right they are, the longer it takes. n is the size of the input. Big O notation uses these functions to describe algorithm efficiency.
Dependency Injection
Dependency Injection(DI) is a software engineering technique for defining the dependencies among objects. Basically, the process of supplying a resource that a given piece of code requires. The required resource is called dependency.
There are various classes and objects defined when writing code. Most of the time, these classes depend on other classes in order to fulfill their intended purpose.
DI handles defining these dependent resources and provides ways to instantiate or create them externally.
In other words, if object A depends on object B, object A must not create import object B directly. Instead of this, object A must provide a way for injecting object B.
Implementing DI in Python
Dependency Injection in Python is a little different from general static language DI. Python has a microframework library for DI, called dependency_injector. This package has two main entities: containers and providers.
Providers describe how objects are accessed. Containers are simply a collection of providers. The most commonly used provider types are: Singleton, Configuration and Factory.
Why use Dependency Injection in your code?
-
Flexibility of configurable components.
-
Helps in Unit testing.
-
High cohesion — Code with reduced module complexity, increased module reusability.
-
Extending the application becomes easier.