Reading-Notes-for-Advanced-Software-Development-in-Python-Course
Linked Lists

A linked list is a sequence of data elements, which are connected together via links. Each data element contains a connection to another data element in form of a pointer. Python does not have linked lists in its standard library. We implement the concept of linked lists using the concept of nodes. Each element of a linked list is called a node, and every node has two different fields:
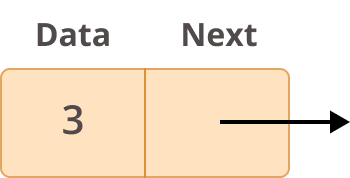
- Data contains the value to be stored in the node.
- Next contains a reference to the next node on the list.
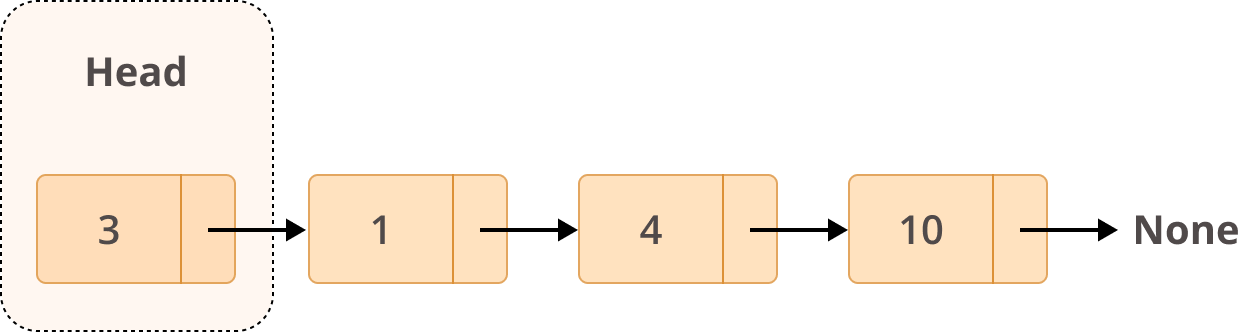
A linked list is a collection of nodes. The first node is called the head, and it’s used as the starting point for any iteration through the list. The last node must have its next reference pointing to None to determine the end of the list.
Why Linked List?
Arrays can be used to store linear data of similar types, but arrays have the following limitations.
- The size of the arrays is fixed: So we must know the upper limit on the number of elements in advance. Also, generally, the allocated memory is equal to the upper limit irrespective of the usage.
- Inserting a new element in an array of elements is expensive because the room has to be created for the new elements and to create room existing elements have to be shifted.
Advantages over arrays:
- Dynamic size
- Ease of insertion/deletion
Creation of Linked list
A linked list is created by using the node class. We create a Node object and create another class to use this ode object. We pass the appropriate values thorugh the node object to point to the next data elements. The below program creates the linked list with three data elements.
class Node:
def __init__(self, dataval=None):
self.dataval = dataval
self.nextval = None
class SLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.headval = None
list1 = SLinkedList()
list1.headval = Node("Mon")
e2 = Node("Tue")
e3 = Node("Wed")
# Link first Node to second node
list1.headval.nextval = e2
# Link second Node to third node
e2.nextval = e3
Traversing a Linked List
Singly linked lists can be traversed in only forwrad direction starting form the first data element. We simply print the value of the next data element by assgining the pointer of the next node to the current data element.
class Node:
def __init__(self, dataval=None):
self.dataval = dataval
self.nextval = None
class SLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.headval = None
def listprint(self):
printval = self.headval
while printval is not None:
print (printval.dataval)
printval = printval.nextval
list = SLinkedList()
list.headval = Node("Mon")
e2 = Node("Tue")
e3 = Node("Wed")
# Link first Node to second node
list.headval.nextval = e2
# Link second Node to third node
e2.nextval = e3
list.listprint()
When the above code is executed, it produces the following result:
Mon
Tue
Wed