Reading-Notes-for-Advanced-Software-Development-in-Python-Course
Python Modules and Packages – An Introduction
Modular programming is a software design technique that emphasizes separating the functionality of a program into independent, interchangeable modules, such that each contains everything necessary to execute only one aspect of the desired functionality.
Python Modules
A module allows you to logically organize your Python code. Grouping related code into a module makes the code easier to understand and use. A module is a Python object with arbitrarily named attributes that you can bind and reference.
To create a module just save the code you want in a file with the file extension .py
Now we can use the module we just created, by using the import statement: import mymodule
Python Packages
As our application program grows larger in size with a lot of modules, we place similar modules in one package and different modules in different packages. This makes a project (program) easy to manage and conceptually clear.
A directory must contain a file named init.py in order for Python to consider it as a package. This file can be left empty but we generally place the initialization code for that package in this file.
Creating a package is quite straightforward, since it makes use of the operating system’s inherent hierarchical file structure.
pytest: helps you write better programs¶
Pytest is a robust Python testing tool, pytest can be used for all types and levels of software testing. pytest can be used by development teams, QA teams, independent testing groups, individuals practicing TDD, and open source projects. In fact, projects all over the Internet have switched from unittest or nose to pytest, including Mozilla and Dropbox. Why? Because pytest offers powerful features such as ‘assert‘ rewriting, a third-party plugin model, and a powerful yet simple fixture model that is unmatched in any other testing framework.
pytest is a software test framework, which means pytest is a command-line tool that automatically finds tests you’ve written, runs the tests, and reports the results.
Testing your code brings a wide variety of benefits. It increases your confidence that the code behaves as you expect and ensures that changes to your code won’t cause regressions. Writing and maintaining tests is hard work, so you should leverage all the tools at your disposal to make it as painless as possible. pytest is one of the best tools you can use to boost your testing productivity.
Assertions in PyTest
Assertions are checks that return either True or False status. In pytest, if an assertion fails in a test method, then that method execution is stopped there. The remaining code in that test method is not executed, and pytest will continue with the next test method. example:
```
assert x==4 is a successful assertion
```
Python Function Recursion
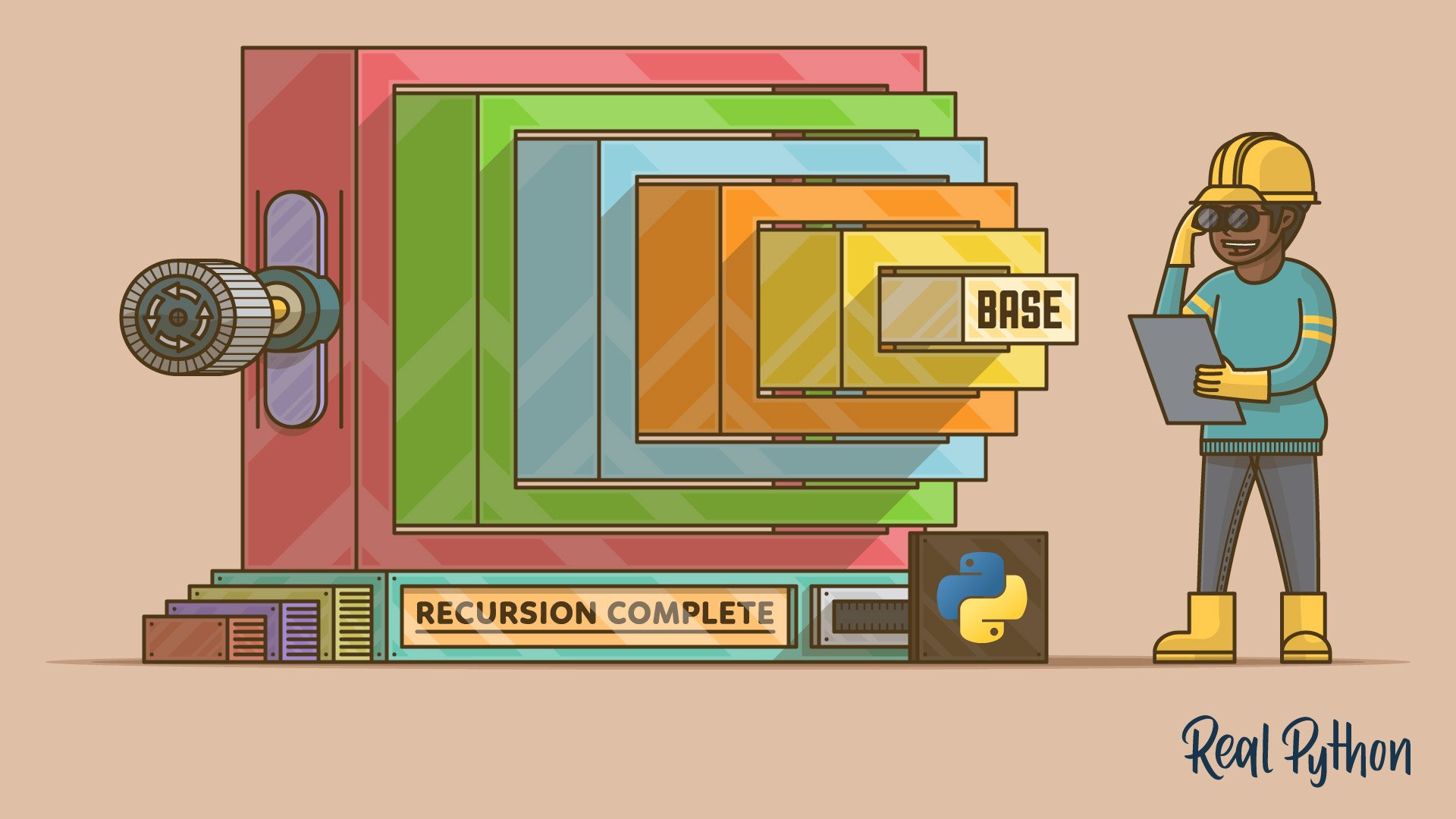
Recursion is a common mathematical and programming concept. It means that a function calls itself. This has the benefit of meaning that you can loop through data to reach a result.
This means that the function will continue to call itself and repeat its behavior until some condition is met to return a result. All recursive functions share a common structure made up of two parts: base case and recursive case.
Behind the scenes, each recursive call adds a stack frame (containing its execution context) to the call stack until we reach the base case. Then, the stack begins to unwind as each call returns its results.
Recursive functions are common in computer science because they allow programmers to write efficient programs using a minimal amount of code. The downside is that they can cause infinite loops and other unexpected results if not written properly.