Reading-Notes-for-Advanced-Software-Development-in-Python-Course
Cryptography
Cryptography is a method of protecting information and communications through the use of codes, so that only those for whom the information is intended can read and process it. The prefix “crypt-“ means “hidden” or “vault” – and the suffix “-graphy” stands for “writing.”
In computer science, cryptography refers to secure information and communication techniques derived from mathematical concepts and a set of rule-based calculations called algorithms, to transform messages in ways that are hard to decipher. These deterministic algorithms are used for cryptographic key generation, digital signing, verification to protect data privacy, web browsing on the internet, and confidential communications such as credit card transactions and email.
The Caesar Cipher technique is one of the earliest and simplest method of encryption technique. It’s simply a type of substitution cipher, i.e., each letter of a given text is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example with a shift of 1, A would be replaced by B, B would become C, and so on. The method is apparently named after Julius Caesar, who apparently used it to communicate with his officials.
Thus to cipher a given text we need an integer value, known as shift which indicates the number of position each letter of the text has been moved down. The encryption can be represented using modular arithmetic by first transforming the letters into numbers, according to the scheme, A = 0, B = 1,…, Z = 25. Encryption of a letter by a shift n can be described mathematically as.
E_n(x)=(x+n)mod\ 26 (Encryption Phase with shift n)
D_n(x)=(x-n)mod\ 26 (Decryption Phase with shift n)
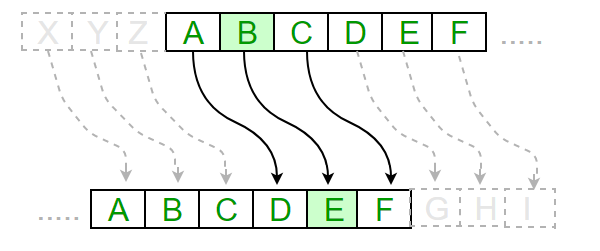
Algorithm for Caesar Cipher:
Input:
- A String of lower case letters, called Text.
- An Integer between 0-25 denoting the required shift.
Procedure:
- Traverse the given text one character at a time .
- For each character, transform the given character as per the rule, depending on whether we’re encrypting or decrypting the text.
- Return the new string generated.